02 装饰器
1.ES6基础
1.1 原型链
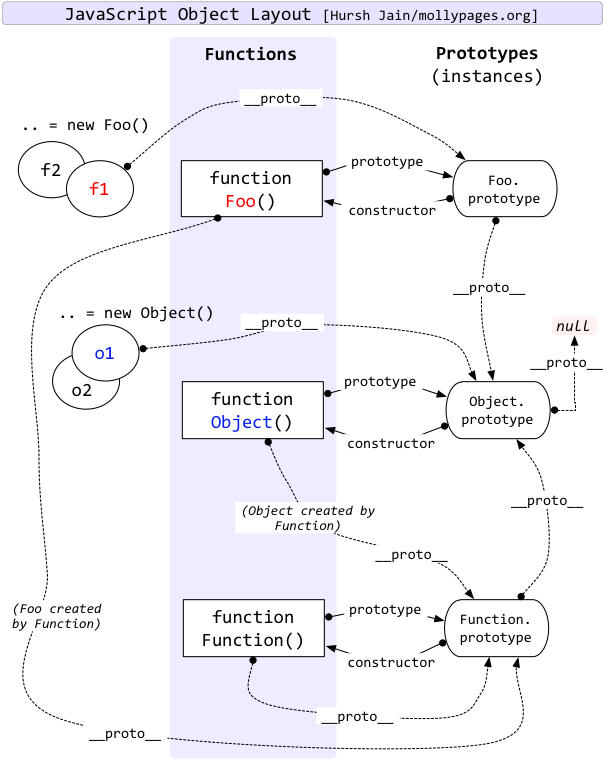 这张图展示了 JavaScript 中函数和原型对象之间的关系,揭示了它们在原型链上的互相连接。通过这个图来理解 JavaScript 中的对象和函数是如何通过原型链连接在一起的 主要部分
这张图展示了 JavaScript 中函数和原型对象之间的关系,揭示了它们在原型链上的互相连接。通过这个图来理解 JavaScript 中的对象和函数是如何通过原型链连接在一起的 主要部分
- Functions:
- 表示函数对象,图中展示了Foo、Object 和 Function对象
- 函数对象通过 prototype 属性指向其原型对象
- Prototypes(instances):
- 表示由函数对象创建的实例对象,通过 new 操作符创建。
- 原型对象有一个 constructor 属性指向创建它的函数对象,并通过 proto 属性链接到原型链上的下一个对象。 详细解析
- 函数Foo()和示例f1
- f1 = new Foo() 创建了 f1 实例。
- f1 的 proto 属性指向 Foo.prototype。
- Foo 函数对象的 prototype 属性指向 Foo.prototype。
- Foo.prototype 的 constructor 属性指向 Foo 函数对象。
- 函数 Object() 和实例 o1、o2:
- o1 = new Object() 和 o2 = new Object() 创建了 o1 和 o2 实例。
- o1 和 o2 的 proto 属性指向 Object.prototype。
- Object 函数对象的 prototype 属性指向 Object.prototype。
- Object.prototype 的 constructor 属性指向 Object 函数对象。
- Object.prototype.proto 指向 null,表示原型链的终点。
- 函数 Function() 和函数对象 Foo、Object:
- Foo 和 Object 函数对象是由 Function 构造函数创建的。
- Foo.proto 和 Object.proto 指向 Function.prototype。
- Function 函数对象的 prototype 属性指向 Function.prototype。
- Function.prototype 的 constructor 属性指向 Function 函数对象。
- Function.prototype.proto 指向 Object.prototype,连接到一般对象的原型链上。
1.2. Reflect
Reflect 是 ES6 中引入的一个内置对象,它提供了一些反射方法,这些方法与那些在 Object 和 Function 原型上的方法具有相同的名称和功能。Reflect 的引入主要是为了使操作对象的行为变得更规范和一致,并且提供一个与 Proxy 对象互补的 API。下面是对 Reflect 的详细讲解。
1.2.1 Reflect 的方法
Reflect 对象的方法大致可以分为三类:对象操作、函数调用和原型操作。以下是 Reflect 所提供的所有方法及其说明:
对象操作方法
- Reflect.get(target, propertyKey[, receiver]):获取对象的属性值,相当于 target[propertyKey]。
- Reflect.set(target, propertyKey, value[, receiver]):设置对象的属性值,相当于 target[propertyKey] = value。
- Reflect.deleteProperty(target, propertyKey):删除对象的属性值,相当于 delete target[propertyKey]。
- Reflect.has(target, propertyKey):检查对象是否有某个属性,相当于 propertyKey in target。
- Reflect.defineProperty(target, propertyKey, descriptor):定义对象的属性,相当于 Object.+ defineProperty(target, propertyKey, descriptor)。
- Reflect.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(target, propertyKey):获取对象自有属性的描述符,相当于 Object.+ getOwnPropertyDescriptor(target, propertyKey)。
- Reflect.ownKeys(target):返回对象的所有自有属性的键,相当于 Object.getOwnPropertyNames(target).+ concat(Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(target))。
函数调用方法
- Reflect.apply(target, thisArgument, argumentsList):调用一个函数,相当于 Function.prototype.apply.+ call(target, thisArgument, argumentsList)。
- Reflect.construct(target, argumentsList[, newTarget]):构造一个实例,相当于 new target(...argumentsList)。
原型操作方法
- Reflect.getPrototypeOf(target):获取对象的原型,相当于 Object.getPrototypeOf(target)。
- Reflect.setPrototypeOf(target, prototype):设置对象的原型,相当于 Object.setPrototypeOf(target, + prototype)。
- Reflect.isExtensible(target):检查对象是否是可扩展的,相当于 Object.isExtensible(target)。 Reflect.preventExtensions(target):让一个对象变得不可扩展,相当于 Object.preventExtensions(target)。
1.2.2 具体示例
1.2.2.1 Reflect.get 和 Reflect.set
const obj = { a: 1 };
// 获取对象的属性值
console.log(Reflect.get(obj, 'a')); // 1
// 设置对象的属性值
Reflect.set(obj, 'b', 2);
console.log(obj.b); // 2
1.2.2.2 Reflect.deleteProperty
const obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };
// 删除对象的属性
Reflect.deleteProperty(obj, 'a');
console.log(obj); // { b: 2 }
1.2.2.3 Reflect.has
const obj = { a: 1 };
// 检查对象是否有某个属性
console.log(Reflect.has(obj, 'a')); // true
console.log(Reflect.has(obj, 'b')); // false
1.2.2.4 Reflect.defineProperty
const obj = {};
// 定义对象的属性
Reflect.defineProperty(obj, 'a', {
value: 1,
writable: true,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true
});
console.log(obj.a); // 1
1.2.2.5 Reflect.apply
function sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
// 调用函数
console.log(Reflect.apply(sum, undefined, [1, 2])); // 3
1.2.2.6 Reflect.construct
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 构造实例
const person = Reflect.construct(Person, ['John']);
console.log(person.name); // John
1.2.2.7 Reflect.getPrototypeOf 和 Reflect.setPrototypeOf
const obj = { a: 1 };
const proto = { b: 2 };
// 获取对象的原型
console.log(Reflect.getPrototypeOf(obj)); // {}
// 设置对象的原型
Reflect.setPrototypeOf(obj, proto);
console.log(Reflect.getPrototypeOf(obj)); // { b: 2 }
1.3. reflect-metadata
reflect-metadata 是一个用于 TypeScript 和 ECMAScript 提案的元数据反射库。它通过提供对元数据的定义和检索支持,简化了装饰器(Decorators)的使用。该库实现了多种元数据相关功能,可以在类、方法、参数和属性上设置和获取元数据。
1.3.1 安装
要使用 reflect-metadata,首先需要将其安装到你的项目中。你可以使用 npm 或 yarn 进行安装:
npm install reflect-metadata
或者使用 yarn:
yarn add reflect-metadata
1.3.2 使用方法
在使用 reflect-metadata 之前,需要在代码的入口文件(例如 index.ts 或 main.ts)中引入 reflect-metadata:
import 'reflect-metadata';
1.3.3 主要功能
reflect-metadata 提供了一组用于定义和检索元数据的方法:
- Reflect.defineMetadata(metadataKey, metadataValue, target, propertyKey):定义元数据。
- Reflect.hasMetadata(metadataKey, target, propertyKey):检查目标对象是否具有指定的元数据。
- Reflect.getMetadata(metadataKey, target, propertyKey):获取目标对象的元数据。
- Reflect.getOwnMetadata(metadataKey, target, propertyKey):获取目标对象的自有元数据。
- Reflect.deleteMetadata(metadataKey, target, propertyKey):删除目标对象的元数据。
import 'reflect-metadata';
// 定义一个类
class MyClass {
private myProperty: string;
constructor(value: string) {
this.myProperty = value;
}
// 定义一个方法,并为其添加元数据
@Reflect.metadata('customKey', 'customValue')
myMethod() {
console.log(`Executing myMethod`);
}
}
// 实例化 MyClass
const instance = new MyClass('Hello');
// 1. 定义元数据
Reflect.defineMetadata('key1', 'value1', instance, 'myProperty');
// 2. 检查是否具有指定的元数据
const hasMetadata = Reflect.hasMetadata('key1', instance, 'myProperty');
console.log(`Has metadata 'key1' for 'myProperty': ${hasMetadata}`);
// 3. 获取元数据
const metadataValue = Reflect.getMetadata('key1', instance, 'myProperty');
console.log(`Metadata 'key1' value for 'myProperty': ${metadataValue}`);
// 4. 获取自有元数据(针对方法)
const ownMetadataValue = Reflect.getOwnMetadata('customKey', instance, 'myMethod');
console.log(`Own metadata 'customKey' value for 'myMethod': ${ownMetadataValue}`);
// 5. 删除元数据
Reflect.deleteMetadata('key1', instance, 'myProperty');
const deletedMetadata = Reflect.getMetadata('key1', instance, 'myProperty');
console.log(`Metadata 'key1' after deletion: ${deletedMetadata}`);
2.类
2.1 类的定义
TypeScript 中的类是基于 ECMAScript 2015(ES6)标准的实现,并在其基础上增加了类型支持和其他特性,使得面向对象编程更加完善和强大。以下是 TypeScript 中类的详细讲解。
基本概念
- 类的定义:类是对象的蓝图,定义了对象的属性和方法。
- 构造函数:constructor 是一个特殊的方法,用于在创建对象实例时初始化对象。
- 成员变量:类的属性,可以是实例属性或静态属性。
- 方法:类的行为,可以是实例方法或静态方法。
class Person {
// 实例属性
name: string;
age: number;
// 静态属性
static species: string = 'Homo sapiens';
// 构造函数
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 实例方法
greet(): string {
return `Hello, my name is ${this.name} and I am ${this.age} years old.`;
}
// 静态方法
static speciesInfo(): string {
return `All humans belong to the species ${Person.species}.`;
}
}
// 创建类的实例
const person1 = new Person('John', 30);
// 调用实例方法
console.log(person1.greet()); // 输出: Hello, my name is John and I am 30 years old.
// 调用静态方法
console.log(Person.speciesInfo()); // 输出: All humans belong to the species Homo sapiens.
// 构造函数
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 实例方法
Person.prototype.greet = function () {
return 'Hello, my name is ' + this.name + ' and I am ' + this.age + ' years old.';
};
// 静态属性
Person.species = 'Homo sapiens';
// 静态方法
Person.speciesInfo = function () {
return 'All humans belong to the species ' + Person.species + '.';
};
// 创建类的实例
var person1 = new Person('John', 30);
// 调用实例方法
console.log(person1.greet()); // 输出: Hello, my name is John and I am 30 years old.
// 调用静态方法
console.log(Person.speciesInfo()); // 输出: All humans belong to the species Homo sapiens.
2.2 装饰器
在 TypeScript 中,装饰器是一种特殊类型的声明,它能够附加到类声明、方法、访问符、属性或参数上,可以修改类的行为。装饰器是一个实验性的特性,需要在 tsconfig.json 文件中启用 experimentalDecorators 编译器选项。
2.2.1 装饰器的类型
类装饰器(Class Decorators):应用于类构造函数,可以用于修改类的定义。
方法装饰器(Method Decorators):应用于方法,可以用于修改方法的行为。
访问器装饰器(Accessor Decorators):应用于类的访问器属性(getter 或 setter)。
属性装饰器(Property Decorators):应用于类的属性。
参数装饰器(Parameter Decorators):应用于方法参数。
| 装饰器名称 | 装饰器描述 | 装饰器的参数说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 类装饰器 (Class Decorators) | 应用于类构造函数,可以用于修改类的定义。 | constructor: Function |
| 方法装饰器 (Method Decorators) | 应用于方法,可以用于修改方法的行为。 | target: Object, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor |
| 访问器装饰器 (Accessor Decorators) | 应用于类的访问器属性(getter 或 setter)。 | target: Object, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor |
| 属性装饰器 (Property Decorators) | 应用于类的属性。 | target: Object, propertyKey: string |
| 参数装饰器 (Parameter Decorators) | 应用于方法参数。 | target: Object, propertyKey: string, parameterIndex: number |
2.2.2 类装饰器
2.2.2.1 简单类装饰器
function logClass(constructor: Function) {
console.log("Class created:", constructor.name);
}
@logClass
class Person {
constructor(public name: string) {}
}
// 输出: Class created: Person
2.2.2.2 类装饰器工厂
装饰器工厂是一个返回装饰器函数的函数,可以接受参数来控制装饰器的行为。
function logClassWithParams(message: string) {
return function (constructor: Function) {
console.log(message, constructor.name);
};
}
@logClassWithParams("Creating class:")
class Car {
constructor(public model: string) {}
}
// 输出: Creating class: Car
2.2.2.3 修改类的行为
这个装饰器扩展了类的功能,添加了一个新的属性和方法。
function addTimestamp<T extends { new(...args: any[]): {} }>(constructor: T) {
return class extends constructor {
timestamp = new Date();
};
}
interface Document{
timestamp: Date;
}
@addTimestamp
class Document {
constructor(public title: string) {}
}
const doc = new Document("My Document");
//const doc = new Document("My Document") as Document & { timestamp: Date };
console.log(doc.title); // My Document
console.log(doc.timestamp); // 当前日期和时间
export {}
2.2.2.4 替换类的构造函数
可以通过返回一个新的构造函数来替换原有的构造函数,从而修改类的实例化过程。
function replaceConstructor<T extends { new(...args: any[]): {} }>(constructor: T) {
return class extends constructor {
constructor(...args: any[]) {
super(...args);
console.log("Instance created");
}
};
}
@replaceConstructor
class User {
constructor(public name: string) {}
}
const user = new User("Alice");
// 输出: Instance created
2.2.3 方法装饰器
在 TypeScript 中,方法装饰器(Method Decorators)用于修饰类的方法。它们可以用于修改方法的行为、添加元数据、进行日志记录、权限检查等。方法装饰器的目标是类的方法,其签名为
(target: Object, propertyKey: string | symbol, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) => void | PropertyDescriptor。
2.2.3.1 方法装饰器的语法
方法装饰器是一个接受三个参数的函数:
- target:装饰的目标对象,对于静态成员来说是类的构造函数,对于实例成员是类的原型对象。
- propertyKey:装饰的成员名称。
- descriptor:成员的属性描述符。
2.2.3.2 日志记录
可以在方法调用前后记录日志,跟踪方法调用情况。
function log(target: any, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
const originalMethod = descriptor.value;
descriptor.value = function (...args: any[]) {
console.log(`Calling ${propertyKey} with arguments: ${args}`);
const result = originalMethod.apply(this, args);
console.log(`Result: ${result}`);
return result;
};
return descriptor;
}
class Calculator {
@log
add(a: number, b: number): number {
return a + b;
}
}
const calc = new Calculator();
calc.add(2, 3);
2.2.3.3 权限检查
可以在方法调用前检查用户权限,决定是否允许调用。
function authorize(target: any, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
const originalMethod = descriptor.value;
descriptor.value = function (...args: any[]) {
const user = { roles: ['admin'] };
if (!user.roles.includes('admin')) {
throw new Error("User is not authorized to call this method");
}
return originalMethod.apply(this, args);
};
return descriptor;
}
class AdminPanel {
@authorize
deleteUser(userId: string) {
console.log(`User ${userId} deleted`);
}
}
const adminPanel = new AdminPanel();
adminPanel.deleteUser('123'); // User 123 deleted
2.2.3.4 方法缓存
可以缓存方法的返回结果,以提高性能。
function cache(target: any, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
const originalMethod = descriptor.value;
const cacheMap = new Map<string, any>();
descriptor.value = function (...args: any[]) {
const key = JSON.stringify(args);
if (cacheMap.has(key)) {
return cacheMap.get(key);
}
const result = originalMethod.apply(this, args);
cacheMap.set(key, result);
return result;
};
return descriptor;
}
class MathOperations {
@cache
factorial(n: number): number {
if (n <= 1) {
return 1;
}
return n * this.factorial(n - 1);
}
}
const mathOps = new MathOperations();
console.log(mathOps.factorial(5)); // 120
console.log(mathOps.factorial(5)); // 从缓存中获取结果
2.2.4 访问器装饰器
访问器装饰器(Accessor Decorators)是 TypeScript 中的一种装饰器类型,用于装饰类的访问器属性(getter 和 setter)。访问器装饰器可以用于修改或替换访问器的行为,添加元数据,进行日志记录等。
2.2.4.1 访问器装饰器的语法
访问器装饰器是一个接受三个参数的函数:
target:装饰的目标对象,对于静态成员来说是类的构造函数,对于实例成员是类的原型对象。 propertyKey:访问器的名称。 descriptor:访问器的属性描述符。 访问器装饰器的签名为 (target: Object, propertyKey: string | symbol, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) => void | PropertyDescriptor。
2.2.4.2 日志记录
可以在访问器的 get 和 set 方法中添加日志记录,以跟踪属性的访问和修改。
function log(target: any, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
const originalGet = descriptor.get;
const originalSet = descriptor.set;
if (originalGet) {
descriptor.get = function() {
const result = originalGet.apply(this);
console.log(`Getting value of ${propertyKey}: ${result}`);
return result;
};
}
if (originalSet) {
descriptor.set = function(value: any) {
console.log(`Setting value of ${propertyKey} to: ${value}`);
originalSet.apply(this, [value]);
};
}
return descriptor;
}
class User {
private _name: string;
constructor(name: string) {
this._name = name;
}
@log
get name() {
return this._name;
}
set name(value: string) {
this._name = value;
}
}
const user = new User("Alice");
console.log(user.name); // Getting value of name: Alice
user.name = "Bob"; // Setting value of name to: Bob
console.log(user.name); // Getting value of name: Bob
2.2.4.3 权限控制
可以在访问器中添加权限检查,以控制属性的访问权限。
function adminOnly(target: any, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
const originalGet = descriptor.get;
descriptor.get = function() {
const user = { role: 'user' }; // 示例用户对象
if (user.role !== 'admin') {
throw new Error("Access denied");
}
return originalGet.apply(this);
};
return descriptor;
}
class SecureData {
private _secret: string = "top secret";
@adminOnly
get secret() {
return this._secret;
}
}
const data = new SecureData();
try {
console.log(data.secret); // 抛出错误: Access denied
} catch (error) {
console.log(error.message);
}
2.2.5 属性装饰器
属性装饰器(Property Decorators)是 TypeScript 提供的一种特殊装饰器,用于修饰类的属性。属性装饰器用于添加元数据或进行属性初始化等操作,但不同于方法装饰器和类装饰器,它不能直接修改属性的值或属性描述符。
2.2.5.1 属性装饰器的语法
属性装饰器是一个接受两个参数的函数:
- target:装饰的目标对象,对于静态属性来说是类的构造函数,对于实例属性是类的原型对象。
- propertyKey:装饰的属性名称。 属性装饰器的签名为 (target: Object, propertyKey: string | symbol) => void。
2.2.5.2 元数据添加
属性装饰器常用于添加元数据,可以结合 Reflect API 使用,以便在运行时获取元数据。
import "reflect-metadata";
function required(target: any, propertyKey: string) {
Reflect.defineMetadata("required", true, target, propertyKey);
}
class User {
@required
username: string;
}
function validate(user: User) {
for (let key in user) {
if (Reflect.getMetadata("required", user, key) && !user[key]) {
throw new Error(`Property ${key} is required`);
}
}
}
const user = new User();
user.username = "";
validate(user); // 抛出错误:Property username is required
2.2.5.3 属性访问控制
- 可以使用属性装饰器来定义属性的访问控制或初始值设置。
function defaultValue(value: string) {
return function (target: any, propKey: string) {
let val = value;
const getter = function () {
return val;
};
const setter = function (newVal) {
val = newVal;
};
Object.defineProperty(target, propKey, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: getter,
set: setter,
});
};
}
class Settings {
@defaultValue("dark")
theme: string;
}
const s1 = new Settings();
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(Object.getPrototypeOf(s1), "theme"));//有值
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(s1, "theme"));//undefined
console.log(s1.theme, "--theme");//dark --theme
- 请注意上述写法仅限于target为ES2015时可用,因为在老版本中类的属性是放在原型对象上的
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2015"
}
}
- 对于版本无效,因为在新版本中,类的属性是放在类的实例上的
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ESNext",
}
}
- 如果是新版本的话就需要使用类装饰器了
function defaultValues(defaults: { [key: string]: any }) {
return function <T extends { new(...args: any[]): {} }>(constructor: T) {
return class extends constructor {
constructor(...args: any[]) {
super(...args);
Object.keys(defaults).forEach(key => {
if (this[key] === undefined) {
this[key] = defaults[key];
}
});
}
}
}
}
@defaultValues({
theme: "dark",
})
class Settings {
theme: string;
}
const s1 = new Settings();
console.log(s1.theme); // 输出应该是 "dark"
2.2.5.4 注意事项
不可直接修改属性值: 属性装饰器不能直接修改属性值或描述符,只能用于添加元数据或做一些初始化操作。
配合其他装饰器使用: 属性装饰器通常与其他类型的装饰器(如方法装饰器、类装饰器)配合使用,以实现更复杂的功能。
2.2.6 参数装饰器
参数装饰器(Parameter Decorators)是 TypeScript 中的一种装饰器类型,用于修饰类构造函数或方法的参数。参数装饰器主要用于为参数添加元数据,以便在运行时能够获取这些元数据并进行相应的处理。与其他装饰器不同,参数装饰器不直接修改参数的行为或值。
2.2.6.1 参数装饰器的语法
参数装饰器是一个接受三个参数的函数:
- target:装饰的目标对象,对于静态成员来说是类的构造函数,对于实例成员是类的原型对象。
- propertyKey:参数所属的方法的名称。
- parameterIndex:参数在参数列表中的索引。 参数装饰器的签名为 (target: Object, propertyKey: string | symbol, parameterIndex: number) => void。
2.2.6.2 参数验证
可以使用参数装饰器在方法调用时验证参数的值。
// 引入 reflect-metadata 库,用于反射元数据操作
import "reflect-metadata";
// 参数装饰器函数,用于验证方法参数
function validate(target: any, propertyKey: string, parameterIndex: number) {
// 获取现有的必需参数索引数组,如果不存在则初始化为空数组
const existingRequiredParameters: number[] = Reflect.getOwnMetadata("requiredParameters", target, propertyKey) || [];
// 将当前参数的索引添加到必需参数索引数组中
existingRequiredParameters.push(parameterIndex);
// 将更新后的必需参数索引数组存储到方法的元数据中
Reflect.defineMetadata("requiredParameters", existingRequiredParameters, target, propertyKey);
}
// 方法装饰器函数,用于在方法调用时验证必需参数
function validateParameters(target: any, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
// 保存原始方法
const method = descriptor.value;
// 修改方法,使其在调用时验证必需参数
descriptor.value = function (...args: any[]) {
// 获取方法的必需参数索引数组
const requiredParameters: number[] = Reflect.getOwnMetadata("requiredParameters", target, propertyKey) || [];
// 遍历必需参数索引数组,检查相应的参数是否为 undefined
for (let parameterIndex of requiredParameters) {
if (args[parameterIndex] === undefined) {
// 如果必需参数为 undefined,则抛出错误
throw new Error(`Missing required argument at position ${parameterIndex}`);
}
}
// 调用原始方法并返回其结果
return method.apply(this, args);
};
}
// 定义 User 类
class User {
// 构造函数,初始化 name 属性
constructor(private name: string) {}
// 使用 validateParameters 方法装饰器装饰 setName 方法
@validateParameters
setName(@validate newName: string) {
// 设置新的 name 属性值
this.name = newName;
}
}
// 创建一个 User 实例
const user = new User("Alice");
// 调用 setName 方法,传入有效参数
user.setName("Bob"); // 正常
// 调用 setName 方法,传入 undefined 作为参数,触发参数验证错误
user.setName(undefined); // 抛出错误: Missing required argument at position 0
// 导出一个空对象,以避免模块级别作用域污染
export {}
2.2.6.4 注意事项
只能用于参数: 参数装饰器只能应用于方法的参数,不能应用于类或属性。
依赖反射元数据: 参数装饰器通常依赖 Reflect API 来存储和访问元数据,因此需要引入 reflect-metadata 库,并在 tsconfig.json 中启用 emitDecoratorMetadata 选项。
2.2.7 各种装饰器的执行顺序
执行顺序
- 属性装饰器(Property Decorators)和方法装饰器(Method Decorators)以及访问器装饰器(Accessor Decorators)
- 按照它们在类中出现的顺序,从上到下依次执行。
- 参数装饰器(Parameter Decorators)
- 在执行方法装饰器之前执行,按照参数的位置从右到左依次执行。
- 对于同一个参数的多个装饰器,也是从从右向左依次执行
- 类装饰器(Class Decorators)
- 最后执行。
示例代码及执行顺序
以下是一个示例代码,展示了各种装饰器的执行顺序:
function classDecorator() {
return function (constructor: Function) {
console.log('Class decorator');
};
}
function methodDecorator() {
return function (target: any, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
console.log('Method decorator');
};
}
function accessorDecorator() {
return function (target: any, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
console.log('Accessor decorator');
};
}
function propertyDecorator() {
return function (target: any, propertyKey: string) {
console.log('Property decorator');
};
}
function parameterDecorator() {
return function (target: any, propertyKey: string, parameterIndex: number) {
console.log('Parameter decorator');
};
}
@classDecorator()
class Example {
@propertyDecorator()
prop: string;
@accessorDecorator()
get myProp() {
return this.prop;
}
@methodDecorator()
method(@parameterDecorator() param: any) {
console.log('Method execution');
}
}
执行顺序的输出
Property decorator
Accessor decorator
Parameter decorator
Method decorator
Class decorator
function parameter1Decorator1() {
return function (target: any, propertyKey: string, parameterIndex: number) {
console.log('parameter1Decorator1');
};
}
function parameter1Decorator2() {
return function (target: any, propertyKey: string, parameterIndex: number) {
console.log('parameter1Decorator2');
};
}
function parameter2Decorator1() {
return function (target: any, propertyKey: string, parameterIndex: number) {
console.log('parameter2Decorator1');
};
}
function parameter2Decorator2() {
return function (target: any, propertyKey: string, parameterIndex: number) {
console.log('parameter2Decorator2');
};
}
class Example {
method(
@parameter1Decorator1() @parameter1Decorator2()param1,
@parameter2Decorator1() @parameter2Decorator2()param2
) {
console.log('Method execution');
}
}
执行顺序的输出
parameter2Decorator2
parameter2Decorator1
parameter1Decorator2
parameter1Decorator1
 疾风浴雪
疾风浴雪